Sws101_trafficanalysis
Topic: Traffic Analysis Essentials
Introduction
Focus: Investigating network data to identify problems and anomalies.
Learning Objectives:
- Gain foundational knowledge of network security and traffic analysis.
- Grasp essential concepts for traffic/packet analysis.
Network Security and Network Data
Network Security
Network security relies on two pillars: authentication (who you are) and authorization (what you can do). Various tools and strategies go beyond these to ensure continuous and reliable protection. Network security operations use three levels of control (prevention, detection, correction) for maximum security.
Base Network Security Control Levels:
| Security Control | Description |
|---|---|
| Physical | Physical security controls prevent unauthorized physical access to networking devices, cable boards, locks, and all linked components. |
| Technical | Data security controls prevent unauthorized access to network data, like installing tunnels and implementing security layers. |
| Administrative | Administrative security controls provide consistency in security operations like creating policies, access levels, and authentication processes. |
The most common elements used in network security operations are:
| Access Control | Threat Control |
|---|---|
| The starting point of Network Security. It is a set of controls to ensure authentication and authorization. | Detecting and preventing anomalous/malicious activities on the network. It contains both internal (trusted) and external traffic data probes. |
The key elements of Access Control:
| Security Control | Description |
|---|---|
| Firewall Protection | Controls incoming and outgoing network traffic with predetermined security rules. Designed to block suspicious/malicious traffic and application-layer threats while allowing legitimate and expected traffic. |
| Network Access Control (NAC) | Controls the devices’ suitability before access to the network. Designed to verify device specifications and conditions are compliant with the predetermined profile before connecting to the network. |
| Identity and Access Management (IAM) | Controls and manages the asset identities and user access to data systems and resources over the network. |
| Load Balancing | Controls the resource usage to distribute (based on metrics) tasks over a set of resources and improve overall data processing flow. |
| Network Segmentation | Creates and controls network ranges and segmentation to isolate the users’ access levels, group assets with common functionalities, and improve the protection of sensitive/internal devices/data in a safer network. |
| Virtual Private Networks (VPN) | Creates and controls encrypted communication between devices (typically for secure remote access) over the network (including communications over the internet). |
| Zero Trust Model | Suggests configuring and implementing the access and permissions at a minimum level (providing access required to fulfil the assigned role). The mindset is focused on: “Never trust, always verify”. |
The key elements of Threat Control:
| Security Control | Description |
|---|---|
| Intrusion Detection and Prevention (IDS/IPS) | Inspects the traffic and creates alerts (IDS) or resets the connection (IPS) when detecting an anomaly/threat. |
| Data Loss Prevention (DLP) | Inspects the traffic (performs content inspection and contextual analysis of the data on the wire) and blocks the extraction of sensitive data. |
| Endpoint Protection | Protecting all kinds of endpoints and appliances that connect to the network by using a multi-layered approach like encryption, antivirus, antimalware, DLP, and IDS/IPS. |
| Cloud Security | Protecting cloud/online-based systems resources from threats and data leakage by applying suitable countermeasures like VPN and data encryption. |
| Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) | Technology that helps threat detection, compliance, and security incident management, through available data (logs and traffic statistics) by using event and context analysis to identify anomalies, threats, and vulnerabilities. |
| Security Orchestration Automation and Response (SOAR) | Technology that helps coordinate and automates tasks between various people, tools, and data within a single platform to identify anomalies, threats, and vulnerabilities. It also supports vulnerability management, incident response, and security operations. |
| Network Traffic Analysis & Network Detection and Response | Inspecting network traffic or traffic capture to identify anomalies and threats. |
Managed Security Services
Smaller organizations often lack resources for dedicated security teams (budget, skills, size). Managed Security Services (MSS) fill this gap by outsourcing security operations to Managed Security Service Providers (MSSPs). MSS are cost-effective, flexible (in-house or outsourced), and simplify security management. We’ll explore common MSS elements next.
| Security Control | Description |
|---|---|
| Network Penetration Testing | Assessing network security by simulating external/internal attacker techniques to breach the network. |
| Vulnerability Assessment | Assessing network security by discovering and analysing vulnerabilities in the environment. |
| Incident Response | An organised approach to addressing and managing a security breach. It contains a set of actions to identify, contain, and eliminate incidents. |
| Behavioural Analysis | An organised approach to addressing system and user behaviours, creating baselines and traffic profiles for specific patterns to detect anomalies, threats, vulnerabilities, and attacks. |
Traffic Analysis
Traffic analysis involves capturing and examining network data to identify issues and threats. It’s a valuable tool for both network security (detecting suspicious activity) and operations (monitoring performance and system health). This rich source of network data helps ensure smooth operation and identify potential problems.
There are two main techniques used in Traffic Analysis:
Flow Analysis - collects information from network devices, but unlike packet analysis, it doesn’t delve into the individual details of each packet. This approach offers a more high-level view of network traffic patterns and trends.
Packet Analysis - analyzes every detail within network packets to identify and block suspicious or malicious activity. It essentially captures all available network data and performs a deep dive into each packet’s content.
Answer the questions below
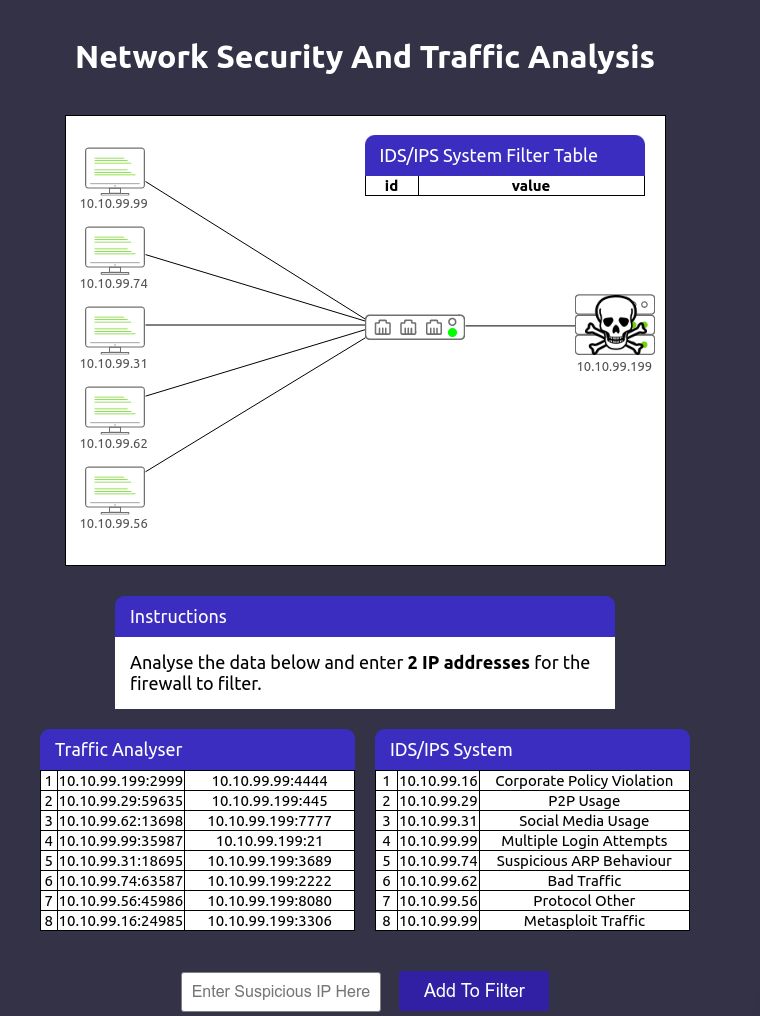
Level-1 is simulating the identification and filtering of malicious IP addresses.
So here we are give a machine to identify and filter the malicious IP address.
Here we identified two ip address 8 and 6
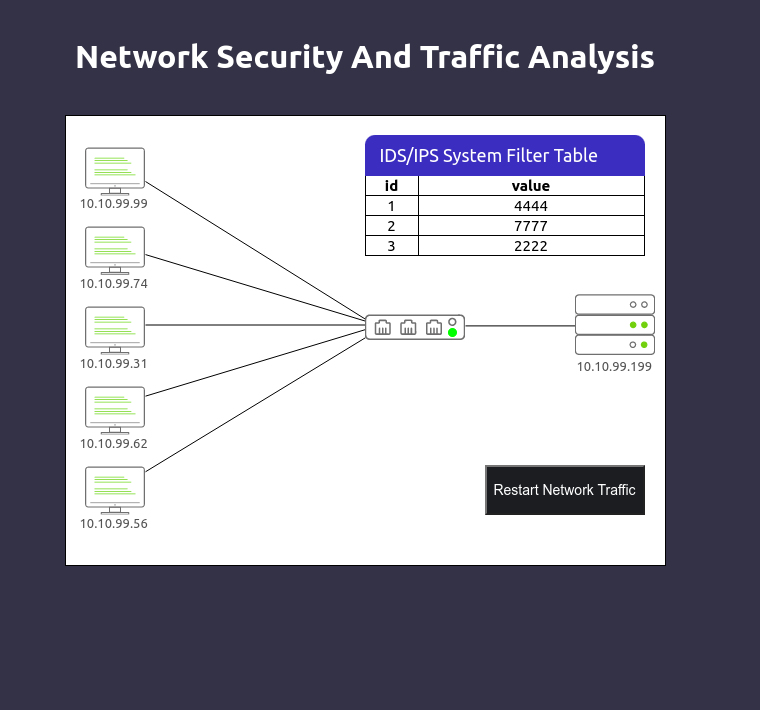
Level-2 is simulating the identification and filtering of malicious IP and Port addresses.
Here we filtered the the ports of the malicious IP address.
Conclusion
In this room we completed the basic fundamentals of network security and traffic analysis, techniques used in traffic analysis which are flow analysis and packet analysis.