Dbs101_flippedclas9
Topic: Query Optimization
In our flipped class nine, we learned about query optimization. Here we learned about Materialised Views and Advanced Topics in Query Optimization. What i understood about query optimization is that it is a process used in DBMS to improve the performance of queries. It finds the most efficient way to retrieve the data you need from a database.
We were divided into groups of 6 in to four groups and two groups were given he same topic and asked to make quiz questions to ask to the other group. After discussing our topic in the home group, the groups with different topics gathered to discuss their topic with the other groups. The first group and our second group gathered together to share our topics.The first group shared about:
Materialised Views
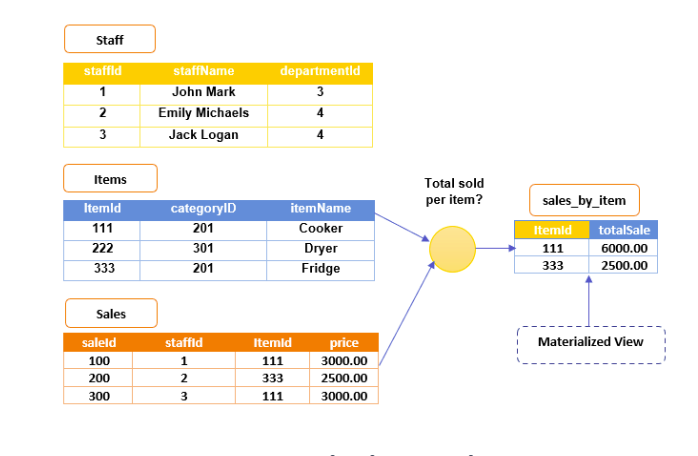
From what the first group shared about materialised view, i learned that it is a pre-computed snapshot of the results of a frequently executed query. It acts like a cached version of the query result, stored within the database itself.
How it functions
When a materialized view is created, the database executes the original query and stores the results as a separate table-like structure. Queries that match the materialized view can retrieve the results directly from the view instead of executing the original query again.
Advantages
- materialized views improves response times for frequently used queries. This is useful for complex queries that involve joins, aggregations, or filtering large datasets.
- the original query doesn’t need to be executed repeatedly, which reduces the amount of work on the database system.
- materialized views can simplify complicated queries for users or applications. Instead of writing complex queries, users can directly access the pre-computed results through a simpler view definition.
Then we shared our view on our topic:
Advanced topics in query optimization
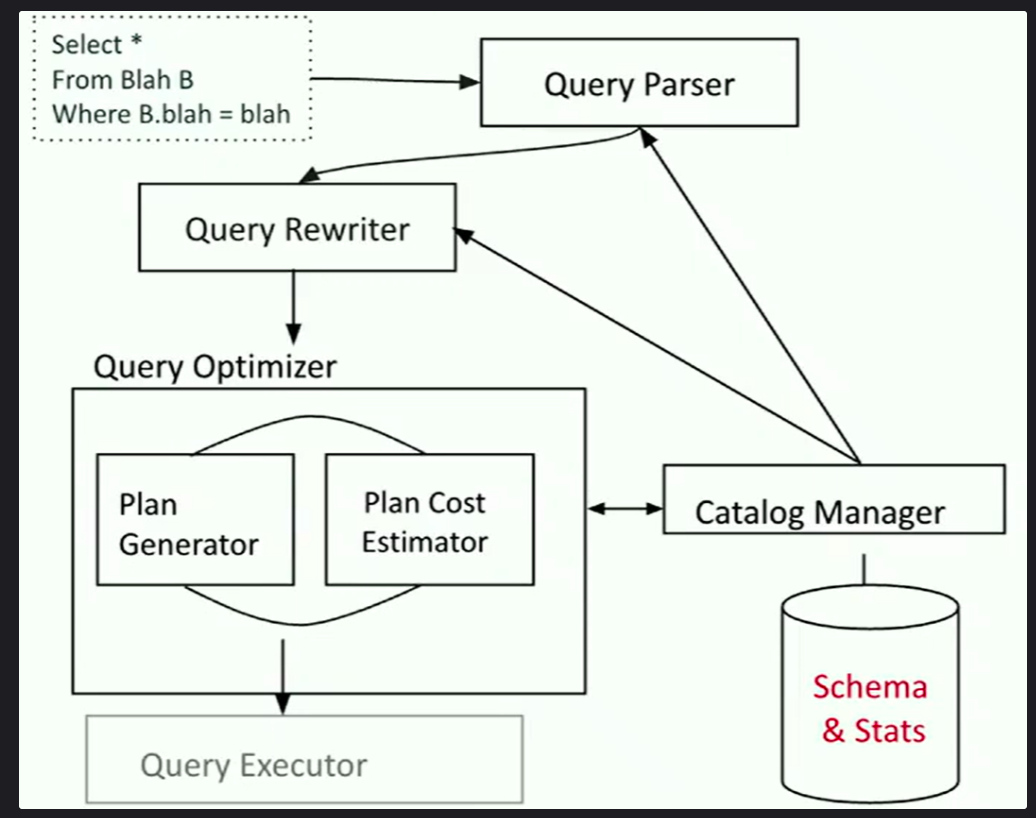
Cost Estimation
- considering various factors like IO cost, CPU cost, and using appropriate cost measure, the database optimizer can choose the most efficient plan for executing a query.
- Understanding cost estimation helps us write better queries and database administrators optimize database performance.
Multi-Query Optimization (MQO)
- Reusing intermediate results: If one query’s output can be used by the next queries, MQO avoids extra processing.
- Batching operations: Combining multiple smaller operations into a single larger one can improve efficiency.
Statistics and Cardinality Estimation
- Accurate data distribution statistics and estimated row counts for tables (cardinality) are crucial for cost estimation.
- Knowing how many rows a filter or join might eliminate helps the optimizer choose the best plan.
Partitioning and Parallelism
- For very large datasets, dividing tables into partitions based on specific columns can improve query performance.
- The optimizer can focus only on the relevant partitions during execution, reducing data scanned.
Cost-Based vs. Rule-Based Optimization
- Traditional optimizers might rely on pre-defined rules to choose a query plan.
- Cost-based optimization uses cost estimation to analyze the specific data and workload, leading to better choices for complex queries.