Dbs101_flippedclas10
Topic: database Transaction
learning Outcomes
- Explain database transactions.
- Understand the transaction model.
- Implement transactions in databases.
- Understand ACID transactions.
In this flipped class we learned about transaction
Transaction
What is transaction?
Transaction is a collection of operation executed betweeen the begin transaction and the end transaction.
Transaction properties
ACID Properties
Atomicity: Atomicity guarantees that either all the operations within a transaction are completed successfully, or none of them are applied
Consistency: ensures that data remains valid and accurate after any changes are made.
Isolation: ensures each transaction executes independently, unaffected by others. This prevents messy data conflicts and guarantees each transaction sees a consistent database state.
Durability: Durability guarantees that once a transaction is finalized, the changes are permanently stored even in case of system crashes, power outages, or hardware failures.
Simple Transaction Model
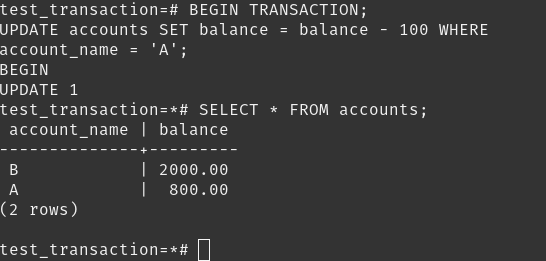
Consider a transaction Ti that transfers $50 from account A to account B
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
Initial values: A = $1000, B = $2000
Transaction Ti
Ti: read(A);
A := A - 50;
write(A); read(B);
B := B + 50;
write(B);
Atomicity Example
Failure occurs after write(A) but before write(B)
- Values: A = $950, B = $2000 (Inconsistent state) Solution: Database system logs old values and restores them on failure
Ensuring Durability
- Write updates to disk before transaction completes.
- Log information to reconstruct updates after failure.
Isolation Example
- Transaction T1 reads A and B, computes A + B.
- Concurrent transaction T2 updates A and B based on inconsistent values.
- Solution: Execute transactions serially or use concurrency control.
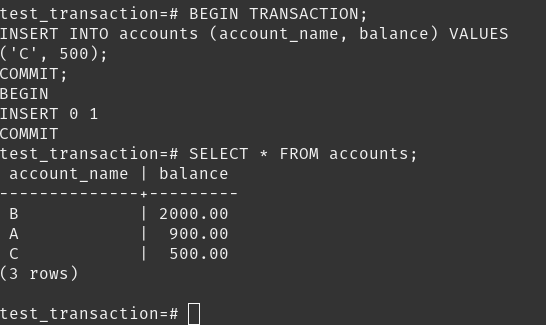
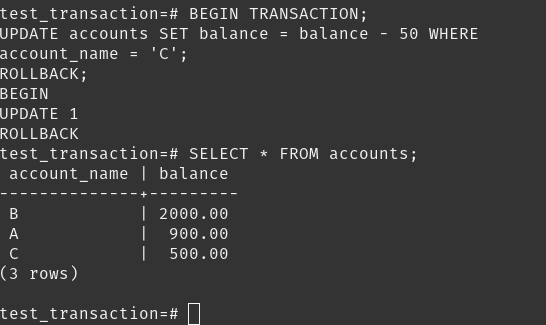
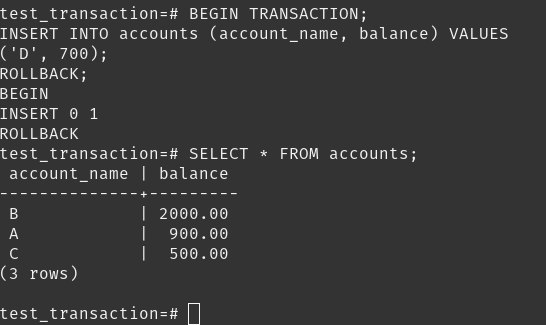
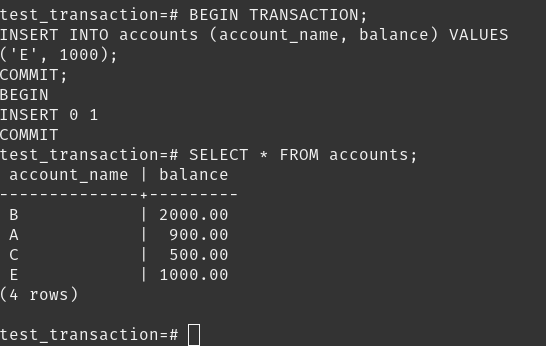
Next we did this transaction in PostgreSQL.
Transaction Atomicity and Durability
- Transactions can fail, but atomicity ensures their effects are completely undone if they don’t finish successfully.
- A recovery scheme manages these failures using a transaction log.
- This log tracks every database change, including the transaction involved, data modified, and old/new values.
- By analyzing the log, the system can redo or undo changes as needed, guaranteeing atomicity and ensuring committed changes are permanent.
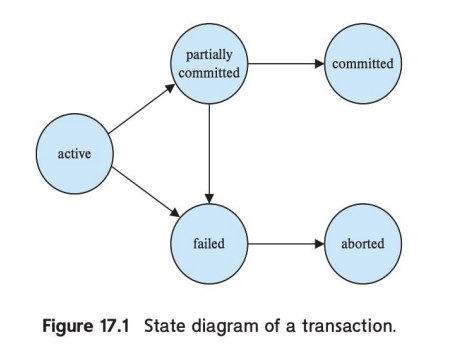
A simple abstract transaction model
1. Active:
2. Partially Committed:
3. Failed
4. Aborted
5. Committed
Serializability
What is serializability?
Serializability makes sure that a non-serial schedule is same as a serial schedule. It checks if the execution of two or more transactions are maintaining the database consistency or not.
Serial Schedule -
A schedule in which only one transaction is executed at a time
Non-serial Schedule -
A schedule where several transactions are executed simultaneously as they are being used in performing real-world database operations. These transactions may be working on the same piece of data.
What is a serializable schedule?
if a non-serial schedule and a serial schedule result in the same then the non-serial schedule is called a serializable schedule.
What is a conflicting pair in transactions?
Two operations inside a schedule are called conflicting if they meet these three conditions:
- They belong to two different transactions.
- They are working on the same data piece.
- One of them is performing the WRITE operation.
Conclusion
Transactions are managed by a specific model within a database system, and we can use commands like COMMIT or ROLLBACK to finalize or undo them.
The ACID properties (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability) are crucial for reliable data changes. Atomicity guarantees all or nothing execution, Consistency keeps data valid, Isolation prevents conflicts between transactions, and Durability ensures changes are permanent.
Understanding transactions and ACID properties is essential for working with databases and maintaining data integrity.